This Help topic provides an example of how class of service (CoS) can be configured on a network to manage bandwidth requirements of network traffic. Before you look at this example, read Getting Started with Class of Service.
In this example, an organization’s network administrator needs to assure that VoIP traffic, both originating in and transiting a network of edge switches and a core router, is configured with appropriate priority, ToS, and queue treatment. We also rate limit the VoIP traffic at the edge to 1 Mb/s to guard against DOS attacks, VoIP traffic into the core at 25 Mb/s, and H.323 call setup at 5 PPS. Data traffic retains the default configuration.
This example assumes CEP authentication using H.323 for VoIP. For networks that do not authenticate VoIP end point with CEP H.323 authentication, the VoIP policy needs to be adjusted accordingly. For instance, SIP uses UDP port 5060, not the TCP port 1720.
To simplify the discussion of the configuration process, this example is limited to the VoIP configuration context. The following table provides a set of sample values for priority, inbound rate limit (IRL), and transmit queue across a number of real world traffic types. This table can be used as an aid in thinking about how you might want to apply CoS across your network. Note that Scavenger class is traffic that should be treated as less than best effort: external web traffic, for instance.
| CoS Name | CoS Index |
Priority | IRL | Transmit Queue | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Queue # | Shaping | Bandwidth | ||||||||
| Edge | Core | Edge | Core | Edge | Core | Edge | Core | |||
| Scavenger (Static) | 0 | 0 | 15 Mb/s | 0 | 0 | 10% | 5% | 5% | ||
| Best Effort (Static) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 80% | 45% | 45% | |||
| Bulk Data (Static) | 2 | 2 | ||||||||
| Critical Data (Static) | 3 | 3 | ||||||||
| Network Control (Static) | 4 | 4 | 40 PPS | 1 Mb/s | 2 | 2 | 1 Mb/s | 25% | 25% | |
| Network Mgmt (Static) | 5 | 5 | 2 Mb/s | |||||||
| RTP/Voice/Video (Static) | 6 | 6 | 1 Mb/s | 25 Mb/s | 3 | 3 | 25% | 25% | ||
| High Priority (Static) | 7 | 7 | ||||||||
| VoIP Call Setup | 8 | 7 | 5 PPS | 3 | 3 | 25% | 25% | |||
The following figure displays the network setup for this example configuration, with the desired Profile/CoS summary for each network device. Each device is configured with VoIP and Data VLANs. Each VoIP VLAN contains four 1‐gigabit interfaces for each device.
CoS VoIP Configuration Example
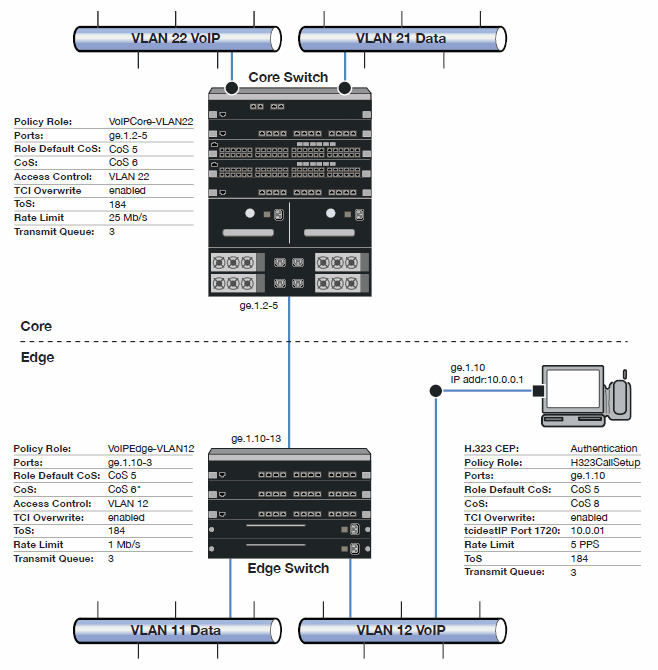
Edge and Core port groups in the RTP/Voice/Video (Static) CoS provide for the difference in rate limiting needs between the end user and aggregation devices. A VoIP Call Setup CoS provides rate limiting for the setup aspect of the VoIP call.
The Edge, Core, and H.323 Call Setup roles are configured with TCI Overwrite, default CoS 5 (best default priority for voice and video), and default access control that contains traffic to the appropriate VLAN.
Use the Policy tab to configure the policy roles and related services using the following instructions. For more information, see How to Create a Class of Service and How to Define Rate Limits.
Configure the Classes of Service
Use the Class of Service tab to configure the static RTP/Voice/Video CoS with the appropriate edge and core rate limits, and create a new CoS for the call setup rate limits.
- For the static RTP/Voice/Video CoS (CoS Index 6):
- Set the ToS to B8.
- Create two new Inbound RL port groups called Edge and Core.
- Set the Edge port group rate limit to 1 Mb/s and the Core port group rate limit to 25 Mb/s. (You can create these rate limits first.)
- Add the appropriate ports to each port group.
- Create a new class of service and name it VoIP Call Setup (CoS Index 8).
- Set the rate limit to 5 PPS for all port groups. (You can create this rate limit first.)
- Set the ToS to B8.
Create the VoIP Core Role
For the core router, create a policy role for VoIP Core. VoIP Core policy deals with packets transiting the core network using VoIP VLAN 22.
- Name the role VoIPCore‐VLAN22.
- Enable TCI overwrite so that ToS is rewritten for this role.
- Set the default access control action to Contain to VLAN 22.
- Set default Class of Service to CoS Index 5.
Create a VoIP Core Service
- Name the service VoIPCore.
- Add the service to the VoIPCore‐VLAN22 role.
Create a Rule
- Create a Layer 2 traffic classification rule for VLAN ID 22 within the VoIPCore service.
- Assign the static RTP/Voice/Video CoS (CoS Index 6) as the Class of Service action for the rule.
Creating the VoIP Edge Role
For the edge switches, create a policy role for VoIP Edge. VoIP Edge policy deals with packets transiting the edge network using VoIP VLAN 12.
- Name the role VoIPEdge‐VLAN12.
- Enable TCI overwrite so that ToS is rewritten for this role.
- Set the default access control action to Contain to VLAN 12.
- Set default Class of Service to CoS Index 5.
Create a VoIP Edge Service
- Name the service VoIPEdge.
- Add the service to the VoIPEdge‐VLAN12 role.
Create a Rule
- Create a Layer 2 traffic classification rule for VLAN ID 12 within the VoIPEdge service.
- Assign the static RTP/Voice/Video CoS (CoS Index 6) as the Class of Service action for the rule.
Creating the H.323 Call Setup Role
The H.323 Call Setup role deals with the call setup traffic for VoIP H.323 authenticated users directly attached to the switch using link ge.1.10.
- Name the role H323CallSetup.
- Enable TCI overwrite so that ToS is rewritten for this policy.
- Set default Class of Service to CoS Index 5.
Create a H.323 Call Setup Service
- Name the service H323CallSetup.
- Add the service to the H323CallSetup role.
Create a Rule
Create a Layer 4 traffic classification rule as follows:
- Traffic Classification Type: IP TCP Port Destination
- Enter in Single Value field: 1720 (TCP Port ID).
- For IP TCP Port Destination value: 10.0.0.1 with a mask of 255.255.255.255.
- Assign the new VoIP Call Setup CoS (CoS Index 8) as the Class of Service action for the rule.
Apply the Roles to Network Devices
After you have created your roles, you must apply them to the network devices as follows:
Core Router
Apply the VoIPCore‐VLAN22 role to ports ge.1.2‐5.
Edge Switch
Apply the VoIPEdge‐VLAN12 role to ports ge.1.10‐13.
Apply the H323CallSetup role to port ge.1.10