This tab lets you view and configure the components of a class of service (CoS). See below for a description of each section. For more information, see How to Create a Class of Service.
Once you have created and defined a class of service, you can then apply it as a classification rule action, as part of the definition of an automated service, or as a role default. For more information, see Getting Started with Class of Service.
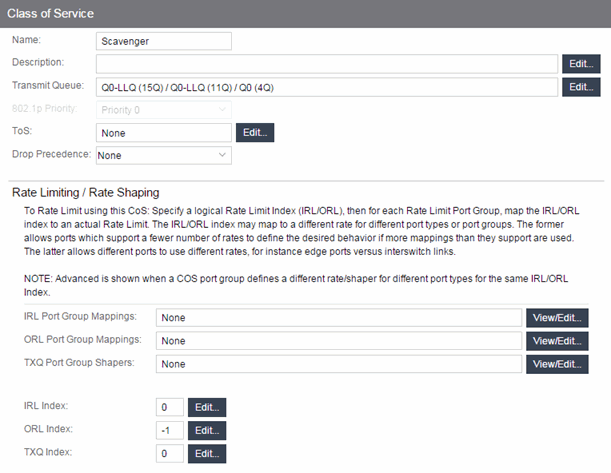
To access this tab, select the Class of Service left-panel tab on the Policy tab. Select a class of service in the tree, and the information for the selected class of service displays in the right panel.
General
- Description
- Use the Edit button to open a window where you can add or modify a description for the class of service.
- Transmit Queue
- This field displays the transmit queue associated with the class of service for each port type. Use the Edit button to display a menu where you can select a new transmit queue, if desired.
- 802.1p Priority
- This drop-down list lets you select the 802.1p priority associated with the class of service, if desired. This field is grayed out for the eight static classes of service provided by the Policy tab (Priority 0-7), because the 802.1p priority cannot be disabled or changed.
- ToS
- Some IP rules enable a ToS value to be written to the ToS field in the IP header of incoming packets. Select the Edit button to open the Edit ToS window, where you can enter a ToS value. The value must be an 8-bit hexadecimal number between 0 and FF (see IP Type of Service for more information).
- Drop Precedence
- The Drop Precedence option is used in conjunction with the Flex-Edge feature available on K-Series and S-Series (Release 7.11 or higher) devices. Flex-Edge provides the unique capability to prioritize traffic in the MAC chip as it enters the switch. When the Class of Service is assigned to a policy role, and that role is applied to a port via a MAC source address mapping or the port default role, the drop precedence dictates the internal priority (within the MAC chip) used for packets received on the port. If congestion occurs, packets with a high drop precedence are discarded first. Therefore, if a packet is important, it should have a low drop precedence. Refer to the K-Series or S-Series Configuration Guide for more information on the Flex-Edge feature and drop precedence.
Rate Limiting/Rate Shaping
This section displays the inbound/outbound rate limits (IRL/ORL) and the outbound transmit queue (TxQ) rate shapers that are configured for the Default port groups associated with the class of service. If you have created additional port groups, the information displays for those groups as well.
With port rate limits, all traffic assigned to this class of service on a given port shares bandwidth specified by the rate limit. Rate shaping paces the rate at which traffic is transmitted out of the transmit queue. You can add or change a rate limit or a rate shaper by double-clicking on the area below a port group name.
If you have ExtremeWireless Controllers (Release 8.01.xx or higher) on your network, you also see the IRL and ORL user rate limits associated with the class of service. User rate limits specify the bandwidth given to each individual user on a port. Currently, user rate limits are only available on wireless controllers.
For more information, see Advanced Rate Limiting by Port Type and How to Configure Transmit Queues.
Index Numbers
At the bottom of the tab there is a section for configuring the rate limit and transmit queue index numbers associated with this class of service. These index numbers are used to map the class of service to the actual rate limits and transmit queue configuration on the device.
Typically, each class of service uses a different index number. The Policy tab automatically assigns these index numbers when you configure a class of services' rate limits and transmit queue shapers. An index number of "-1" indicates that no mappings are associated with the class of service.
All CoS using the same index will use the same rate limit and rate shaping assignments, and thus all traffic using those CoS will share the bandwidth.
- IRL/ORL Index (Inbound/Outbound Rate Limits Index)
- The inbound/outbound port rate limit index associated with the class of service. Index numbers map logical rate limit indexes to the actual physical rate limits you have created in the Policy tab. Select the button to open the Rate Limits selection view window, and select an index for the CoS. For convenience, existing index to rate limit mappings are displayed; if one of the existing indexes is selected, the displayed mappings will apply for this CoS. (Selecting an index highlights all the mappings configured for that index number within the selection view.)
- TxQ Index (Transmit Queue Index)
- The transmit queue index associated with the class of service. Index numbers map logical transmit queue indexes on the ports to the actual physical transmit queues you have configured in the Policy tab. If you have selected an 802.1p priority for this class of service, a default transmit queue index is automatically specified based on the selected priority. You can use the default index or change it according to your own transmit queue configuration. Select the button to open the Transmit Queues selection view window, which lists all the possible transmit queues, organized by index number for each existing port type and group. Selecting an index automatically includes all the transmit queues configured for that index number.
- IUB/OUB Index (Inbound/Outbound User-Based Rates Index)
- If you have ExtremeWireless Controllers (Release 8.01.xx or higher) on your network, you also see the inbound/outbound user rate limits associated with the class of service. User rate limits specify the bandwidth given to each individual user on a port. Currently, user rate limits are only available for these wireless controllers. Select the button to open the Rate Limits selection view window, and select an index for the CoS. For convenience, existing index to rate limit mappings are displayed; if one of the existing indexes is selected, the displayed mappings apply for this CoS. (Selecting an index highlights all the mappings configured for that index number within the selection view.)
- Flood Ctrl Port Groups
- CoS-based flood control is a form of rate limiting that prevents configured ports from being disrupted by a traffic storm, by rate limiting specific types of packets through those ports. When flood control is enabled on a port, incoming traffic is monitored over one second intervals. During an interval, the incoming traffic rate for each configured traffic type (unknown-unicast, broadcast, or multicast) is compared with the configured traffic flood control rate, specified in packets per second. If, during a one second interval, the incoming traffic of a configured type reaches the traffic flood control rate configured on the port, CoS-based flood control drops the traffic until the interval ends. Packets are then permitted to flow again until the limit is again reached.
NOTE: By default, Flood Control is not managed by the Policy tab. To manage flood control configuration on devices in a domain, it can be enabled via the Domain Managed CoS Components drop-down list by selecting All CoS Components or by selecting Flood Control.
For information on related help topics: