Real Capture allows real-time collection of Access Point (AP) wireless traffic for troubleshooting and problem resolution. Real Capture collects traces on the AP wireless interface and transmits them to Wireshark running on a local Windows client. It allows Wireshark to capture RF/wireless traffic as if it were running directly on the AP, providing visibility into network connectivity and performance issues. All Wireshark features are supported, including filters and I/O graphs.
| NOTE: | APs must be running firmware version 8.x or later. The AP2600 series of Access Points does not support the Real Capture feature. |
Real Capture can be enabled for each AP individually from PortView in the ExtremeCloud IQ Site Engine. When it is enabled, Real Capture runs a daemon on the AP that allows it to interface with Wireshark using port 2002 or 2003. The AP then captures all the wireless traffic (except for management traffic) originating from the AP and sends it to Wireshark for analysis.
In addition to capturing network traffic for analysis in Wireshark, the AP also collects RF information. The RADIOTAP header format delivers RF information. You must use Wireshark 1.6 or later to read the full RADIOTAP header information. For troubleshooting features like TxBF/STBC, you can enable capturing the 802.11n preamble header using the AP CLI commands.
| NOTE: | When capturing client traffic on the AP, if the topology is bridged at AP, client traffic is captured and can be analyzed in the resultant trace. However, if the topology is bridged at controller, only WASSP traffic is captured as the AP tunnels this communication back to the controller. This traffic must be sent to the Extreme Networks Support for analysis because it needs to be decoded. In this scenario, it may be better to mirror the switch port where the controller connects to the LAN. |
Configure and Use Real Capture
Use the following steps to configure and use the Real Capture feature.
- Launch ExtremeCloud IQ Site Engine.
- Launch PortView for the AP from the Wireless Client Event History report.
- Select the Wireless tab and then select the Clients tab and the Client Events sub-tab. Right-click on the AP Name and select AP Summary from the menu.
- The AP PortView opens.
NOTE: You can also launch PortView for the AP using the Search tab. Open the Search tab, enter the search criteria (MAC, IP, hostname, or AP serial number) and press Enter to display the AP PortView. - Select the Wireless tab and then select the Clients tab and the Client Events sub-tab. Right-click on the AP Name and select AP Summary from the menu.
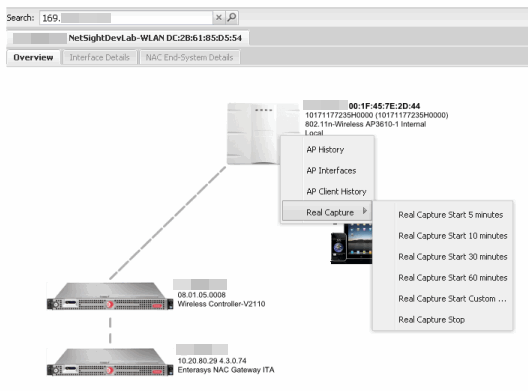
- Right-click on the AP in the PortView topology display and select Real Capture > Real Capture Start xx minutes. Select the desired amount of time to run the capture or create a custom capture duration value. If you need to, you can stop the Real Capture by selecting Real Capture Stop.
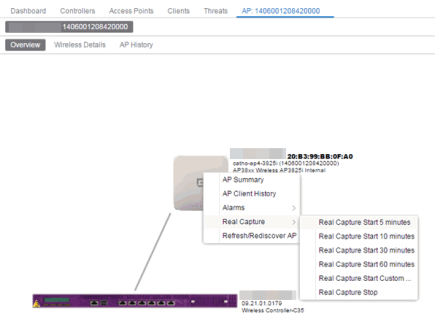
- A message appears to inform you Real Capture has started, and provides a CLI command you can use on a client on which Wireshark is installed, to launch Wireshark against the AP and view the captured traffic.
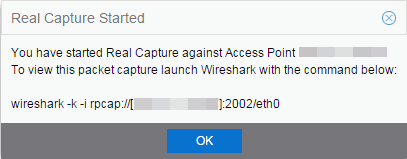
- You can also access the captured traffic in Wireshark using the following steps:
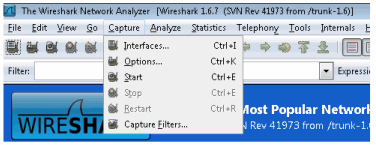
- In Wireshark, select Capture > Options from the menu bar.
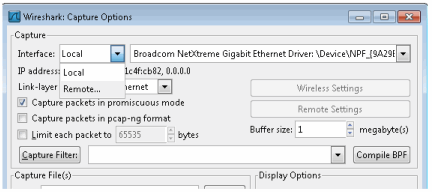
- In the Capture Options window, set the Interface value to Remote.
- The Remote Interface window appears. Enter the AP's IP address in the Host field, and the port number (2002 or 2003) in the Port field (you can see this information in the CLI command message described in step 4). In the Authentication section, select Null authentication. Select OK.
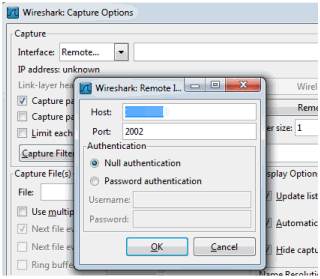
Wireshark adds the command information to the Capture options.
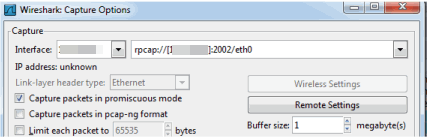
- Select OK in the Capture Options window to begin viewing the captured traffic in Wireshark. When you have the data you need, you can stop the capture and save it to a file for further diagnosis and troubleshooting.
- In Wireshark, select Capture > Options from the menu bar.
Real Capture Example
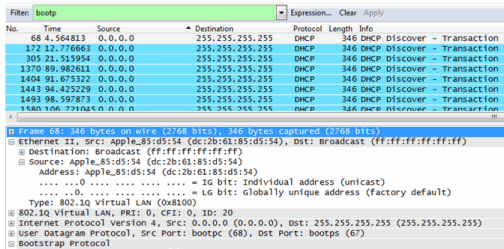
The following example shows how to use Real Capture to diagnose an end-system connection problem in ExtremeCloud IQ Site Engine.
The problem starts when an end-system in ExtremeCloud IQ Site Engine is not able to obtain an IP address.
A search is performed on the 169.x.x.x IP address.
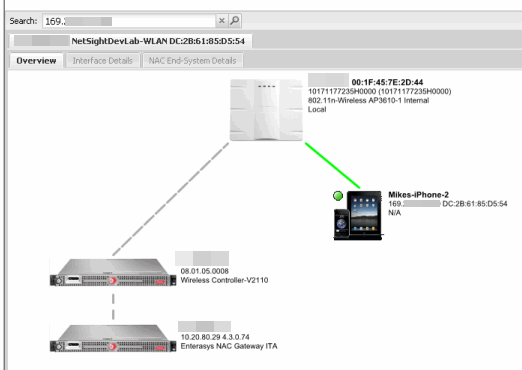
The traffic capture is started on the AP to which the end-system is connected.
The resulting trace in Wireshark shows the end-system sending out DHCP Discover packets with no response, perhaps indicating a VLAN or network-related issue.