ExtremeCloud IQ Site Engine Performance Tuning
The following sections provide detailed information on how to use specific ExtremeCloud IQ Site Engine tools and features to monitor and improve ExtremeCloud IQ Site Engine server performance.
- Tuning NetFlow Collection Settings
- Server Memory Tuning
- Tuning Database Backup Storage
- Binding the Server to One Interface
Tuning NetFlow Collection Settings
NetFlow is a data collection protocol that provides details and analysis of protocol information derived from monitoring flow-based traffic as it traverses a network. K-Series, S-Series, and N-Series devices support NetFlow flow collection. The ExtremeCloud IQ Site Engine server can be configured as a flow collector for the devices on your network using the Flow Sensor Configuration window in Console.
Enabling NetFlow collection on your network can add significant overhead to ExtremeCloud IQ Site Engine server operation. Incoming flow data collection consumes a large portion of server memory and impacts the overall disk utilization footprint of the ExtremeCloud IQ Site Engine server. It can also lead to extended time required to perform an ExtremeCloud IQ Site Engine server backup, if reporting data is included in the backup.
In addition, name resolution for NetFlow traffic displayed in ExtremeCloud IQ Site Engine adds overhead to the server. NetFlow traffic bursts can lead to a spike in name resolution traffic which also adds to the overall load on the network.
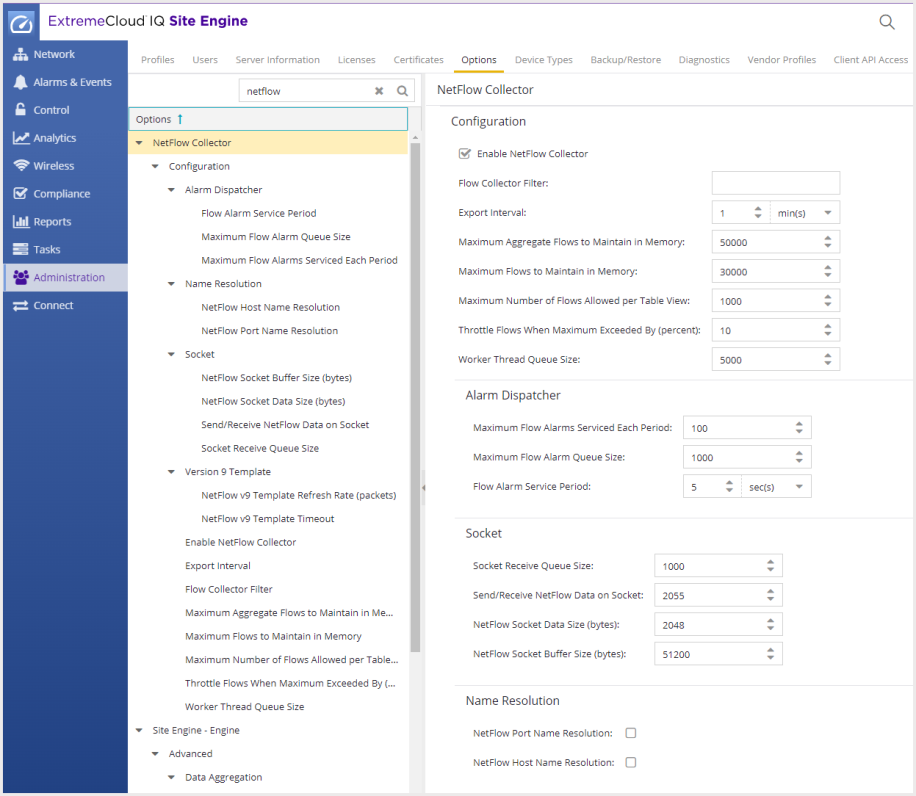
You can adjust NetFlow collection settings using ExtremeCloud IQ Site Engine options. Navigate to
Administration > Options > NetFlow Collector.
For most implementations, the default settings are recommended. However, in some cases, these settings can be adjusted to improve ExtremeCloud IQ Site Engine server performance. For example, you can change the maximum number of flows and aggregate flows to maintain in memory. Changing this number would adjust the amount of memory used to store flows.
You can also disable host and port name resolution for NetFlow. Disabling name resolution would affect the display of ExtremeCloud IQ Site Engine data because IP addresses would not be resolved to names. Other than that, the ExtremeCloud IQ Site Engine data is not impacted. Disabling name resolution would also reduce the DNS traffic on the network and to the DNS server(s).
The Advanced settings for the NetFlow flow collection let you limit resources used by ExtremeCloud IQ Site Engine Flow Alarm handling.
| NOTE: | Perform any change in the default flow collection parameters with caution and make adjustments taking into account items such as the size of the network and features enabled in ExtremeCloud IQ Site Engine. Advise all ExtremeCloud IQ Site Engine users of changes to the default flow collection parameters so that they can monitor any changes in server performance. |
NetFlow Collection Options
Server Memory Tuning
The ExtremeCloud IQ Site Engine software requires a significant amount of system resources. It is intended to run on a dedicated system where it does not compete with other software for system resources. Upon installation, ExtremeCloud IQ Site Engine detects whether the system has the minimum memory required to run correctly. It will then scale its memory usage to take advantage of the available system memory. It should not be necessary to manually adjust memory usage. If you suspect that you are experiencing performance issues related memory usage, contact Global Technical Assistance Center (GTAC).
Tuning Database Backup Storage
The ExtremeCloud IQ Site Engine Server can be configured to run an automated backup on the day(s) of the week and time of your choosing. An up-to-date database backup is an important component to ensuring that critical information pertaining to all ExtremeCloud IQ Site Engine applications is saved and readily available, if needed.
However, while scheduling regular server backups is a best practice, it can lead to unintended side-effects in some environments. For example, backing up multiple copies of the database consumes disk space on the server. Ensuring there is plenty of free space prior to enabling this feature as well as checking the overall size of each backup is helpful in determining whether space issues can become a problem. (See ExtremeCloud IQ Site Engine Server Disk Utilization for more information.)
Another option is to save backups to a separate location such as a network share. It is important to verify periodically that the backups are running as expected and actually completing. You might also schedule quarterly database restores on a lab server to ensure the integrity of the backups.
In addition, the size of the database backup should be checked after major changes to the environment, for instance enabling ExtremeCloud IQ Site Engine data collection or implementing ExtremeControl on the network. If there are concerns regarding the available disk space, place limits on the number of backups saved or adjust the frequency of backups.
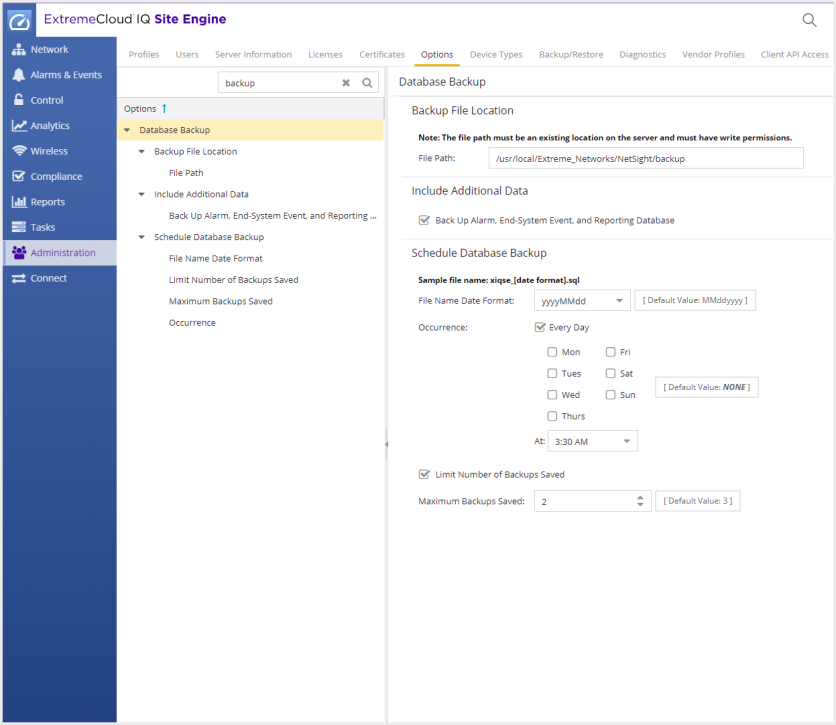
Database backups are configured in the ExtremeCloud IQ Site Engine Suite options. Navigate to
Administration > Options > Database Backup.
Database Backup Options
Binding the Server to One Interface
If the ExtremeCloud IQ Site Engine server has multiple NICs (Network Interface Cards) installed, it is a good practice to configure the server to always bind to the preferred IP address. If the server does not bind to the correct interface, local and remote clients and ExtremeControl engines are unable to connect to the ExtremeCloud IQ Site Engine server.
During the startup process, the ExtremeCloud IQ Site Engine server automatically binds to the first available NIC, which might not be the correct interface for the server to use. In addition, changes on the network can cause the server to bind to an incorrect interface, should the server restart during a change.
You will need to make configuration changes in order to bind the server to the correct interface. Configure the ExtremeCloud IQ Site Engine server to bind to the correct IP address.
For instructions, see the ExtremeCloud IQ Site Engine Installation Guide section on Systems with Multiple NICs.